The world is changing rapidly and is increasingly complex. Higher Education does much more than provide students with disciplinary knowledge. At USask, we prepare strong critical thinkers and successful communicators who can adapt to the needs of the world. The USask Student Competencies form the core foundation of skills, knowledge, and beliefs that students develop through our deliberate teaching and assessment choices. Students become competent because of how we design our courses and programs.
Getting Started: How to Embed USask Student Competencies in your Course.
- Choose a Competency: Many educators are already helping students develop program-level competencies without realizing it. To focus your efforts, choose one competency that best relates to your course. Review the associated rubric to understand what competency looks like at your course level. (links to competencies with icons and corresponding rubrics?, Visual for this process?)
- Choose an approach to your instruction: How we teach significantly impacts students' competency development. When we only cover content, students may learn information temporarily and struggle to apply. Rather than covering content alone, choose one or two changes that fit with the purpose of your course and your teaching philosophy:
- Clearly Define the Competency: Articulate clear, measurable criteria for the competency in your course outcomes.
- Incorporate Experiential Learning: Use case studies, simulations, or project-based tasks to provide authentic contexts for applying theoretical knowledge.
- Encourage Peer Learning and Collaboration: Facilitate collaborative projects or group discussions to develop teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills.
- Integrate Technology and Innovative Teaching Methods: Enhance learning experiences with digital tools, online resources for self-paced learning, or multimedia for engaging content delivery.
- Cultivate a Growth Mindset: Recognize efforts and progress, encouraging students to view challenges as learning opportunities.
- Link Learning to Real-World Applications: Connect course content to current issues, case studies, or industry trends relevant to the competency.
- Adapt your Assessment Methods: To foster deep learning and competency, adapt your assessment methods. Start with one or two changes that align with your course, discipline, and teaching philosophy.
- Offer Personalized Feedback and Support: Provide constructive, personalized feedback, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement to guide students in their learning journey as it relates to the competency.
- Foster Reflective Practices: Encourage reflective essays, journals, or discussions for students to analyze experiences and identify growth areas.
- Utilize Continuous and Formative Assessment: Shift the focus from summative to formative assessments. Use polls, presentations, or portfolio reviews for ongoing feedback and measuring competency development.
- Assess and Reflect on Teaching Practices: Regularly reflect on your teaching, seek feedback, and model ongoing growth to inspire students.
- Use Competency-Based Assessment: Focus on grading competencies directly. Learn more about this approach (link to article) and how to use Canvas for it (link to article).
Remember, the key to developing competencies is to create an engaging, student-centered learning environment reflective of real-world contexts. By implementing these strategies, you can help your students not only acquire knowledge but also develop the skills, perspectives, and understandings necessary for future success.
Deepen Competency Development through Experiential Learning
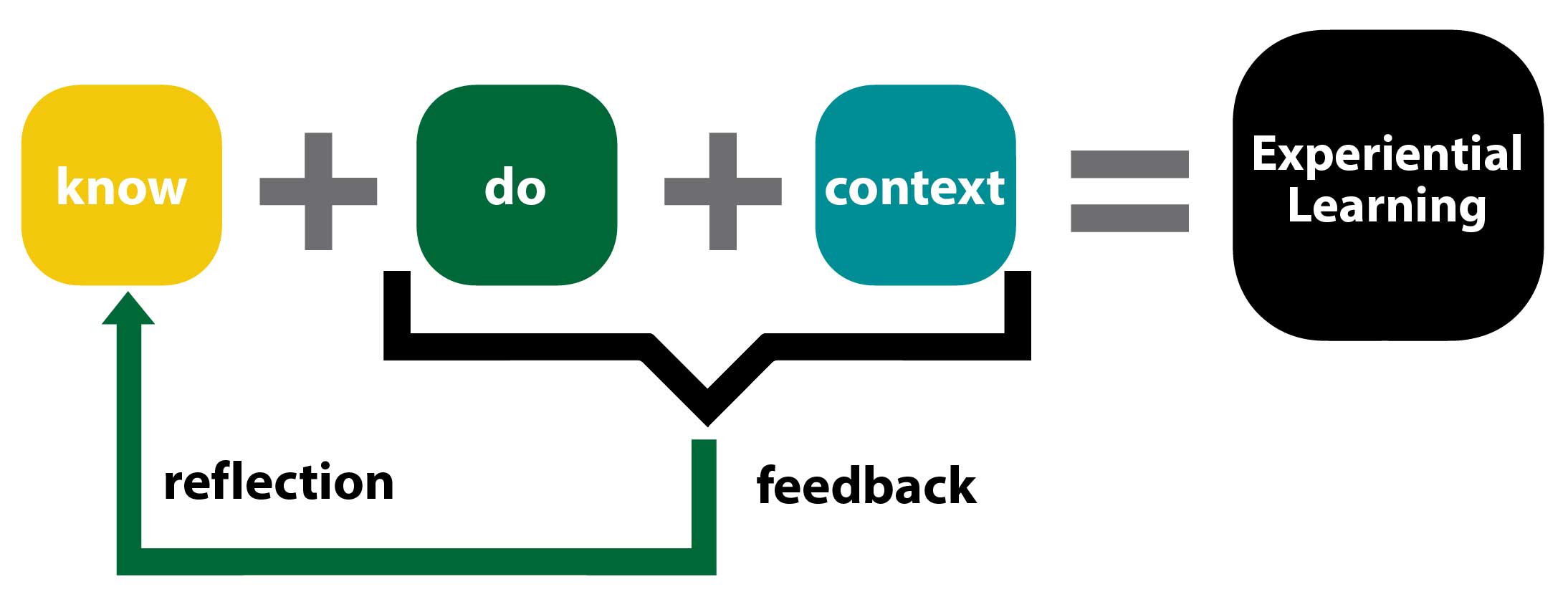
Learners develop competencies through experiential learning, which involves actively applying knowledge in real-world contexts, receiving feedback, and engaging in reflective practice. This process integrates the skills, knowledge, and attributes necessary to address complex challenges and contribute meaningfully to society. It's one of the most effective ways to develop competencies over time. The University of Saskatchewan's Experiential Learning model emphasizes four essential elements:
- Doing: Students actively apply their knowledge in situations with unpredictable elements, requiring decision-making and critical thinking. This active learning involves engaging with real-world problems and scenarios that demand thoughtful application of skills and knowledge.
- Context: Learning takes place within authentic contexts that mirror real-life situations. These contexts provide a rich backdrop for students to navigate, make decisions, and learn from the complexities of actual environments. Examples include working on a project for a real client, addressing a genuine problem, or presenting findings to an external audience.
- Feedback: As students engage in these experiences, they receive timely and relevant feedback on their performance. This feedback is crucial for learning, allowing students to adjust their actions and understandings in response to the challenges they face. It ensures that learning is iterative and responsive, facilitating deeper engagement with the material.
- Reflection: Critical to the experiential learning process is the act of reflection. Students are encouraged to reflect on their experiences, considering what was successful and what could be improved. This reflective practice helps them internalize their learning, understand their strengths and weaknesses, and plan for future growth.
Types of Experiential Learning
Experiential Learning at the University of Saskatchewan includes:
- Case-based learning
- Simulations
- Undergraduate research
- Field-based instruction
- Community-engaged learning
- Clinical placements or practicums
- Study abroad programs
Each type provides unique opportunities for students to engage deeply with their discipline, applying and testing their knowledge and skills in diverse and challenging environments.
Incorporating Experiential Learning into Your Classroom
To integrate Experiential Learning into your curriculum:
- Identify Opportunities: Look for authentic, real-world tasks relevant to your field of study.
- Structure Feedback and Reflection: Create opportunities for timely feedback and reflective practice to enhance learning.
- Align with Competencies: Ensure these experiences align with the competencies students are expected to develop.
This approach enhances academic learning and prepares students for the complexities and demands of the professional world, equipping them with the competencies necessary to contribute meaningfully to society and the global community.
Get Support
Contact gmctl@usask.ca for information about the USask Student Competencies and how to integrate them into your program.

